Low Amniotic Fluid
Low Amniotic Fluid
Low amniotic fluid, medically known as oligohydramnios, refers to a condition where the volume of amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus in the womb is lower than expected for the stage of pregnancy. Amniotic fluid plays a crucial role in fetal development, providing protection, cushioning, and aiding in the exchange of nutrients and waste between the mother and the baby. When levels are too low, it can raise concerns about the health and well-being of the baby.
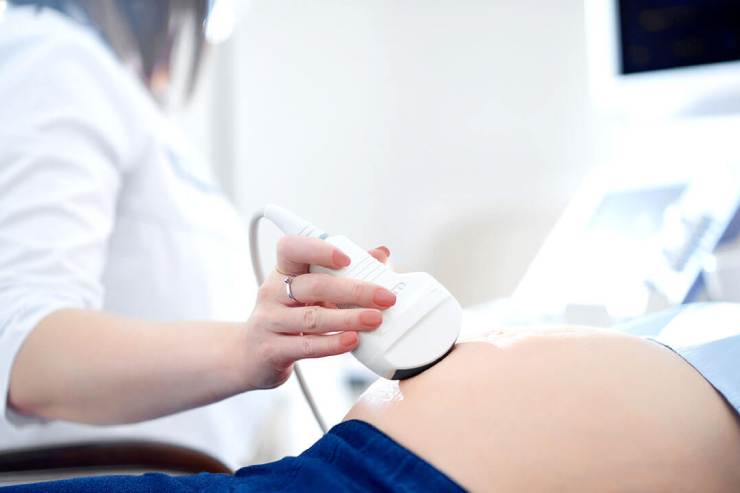
Causes of Low Amniotic Fluid
1. Leakage: Sometimes, a tear in the amniotic membranes can lead to a slow leakage of fluid.
2. Rupture of Membranes: If the membranes rupture prematurely, it can result in a decrease in fluid levels.
3. Maternal Health Conditions: Certain maternal health issues, such as high blood pressure or preeclampsia, can contribute to low amniotic fluid levels.
4. Fetal Kidney Problems: The baby’s inability to produce urine, usually due to kidney problems, can lead to decreased amniotic fluid.
Placental Problems: Issues with the placenta, such as placental insufficiency, can impact the production of amniotic fluid.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
1. Women with low amniotic fluid may not experience any symptoms, or they may notice decreased fetal movement.
2. Diagnosis is typically made through ultrasound, which measures the deepest pocket of amniotic fluid and compares it to standard values for the gestational age.
Risks and Complications
1. Low amniotic fluid can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery, including preterm birth, fetal growth restriction, and umbilical cord compression.
2. It may also lead to developmental issues in the baby, such as lung underdevelopment (pulmonary hypoplasia) or limb deformities.
Management and Treatment
1. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, increasing maternal hydration or bed rest may be recommended.
2. If the condition is severe or poses a risk to the baby, medical interventions such as amnioinfusion (adding fluid into the amniotic sac) or early delivery may be necessary.
About Us
Gynecological consultations at Ashirwad Clinic are a cornerstone of its services. With expertise in addressing a myriad of women's health concerns, the clinic offers a safe and welcoming environment for patients to discuss their needs. Whether it's managing menstrual irregularities, diagnosing PCOD.
Quick Contacts
- Address : Shop No-2, A-53, opposite Patanjali Store, Swarna Jayanti Nagar, Aligarh, Uttar Pradesh 202001
- Phone : +91 7906148352, 9871165086.
- Email : ashirwadclinic@gmail.com
- Country : India
